Tandem Press Brake Working Principle and Applications
In the fast-evolving landscape of modern manufacturing, traditional methods often fall short in meeting demands for speed, precision, and scalability. As industries push for higher efficiency, many companies are turning to advanced equipment like the tandem press brake to streamline their operations. This innovative metal forming technology, also known as a dual-machine linkage bending system, stands out for its ability to handle complex tasks with remarkable accuracy. By synchronizing two or more press brakes, it enables the bending of large-scale metal sheets that would be challenging or impossible with a single machine. In this comprehensive guide, we’ll explore the core mechanics behind tandem press brakes, their key benefits over conventional approaches, real-world uses across various sectors, structural highlights that make them reliable, and a look at their promising future in an increasingly automated world.
Whether you’re a fabricator dealing with oversized components or an engineer seeking ways to optimize production lines, understanding tandem press brakes can unlock new levels of productivity. Drawing from industry insights and practical examples, this article delves into how these machines work and where they shine, helping you evaluate if they’re the right fit for your needs.
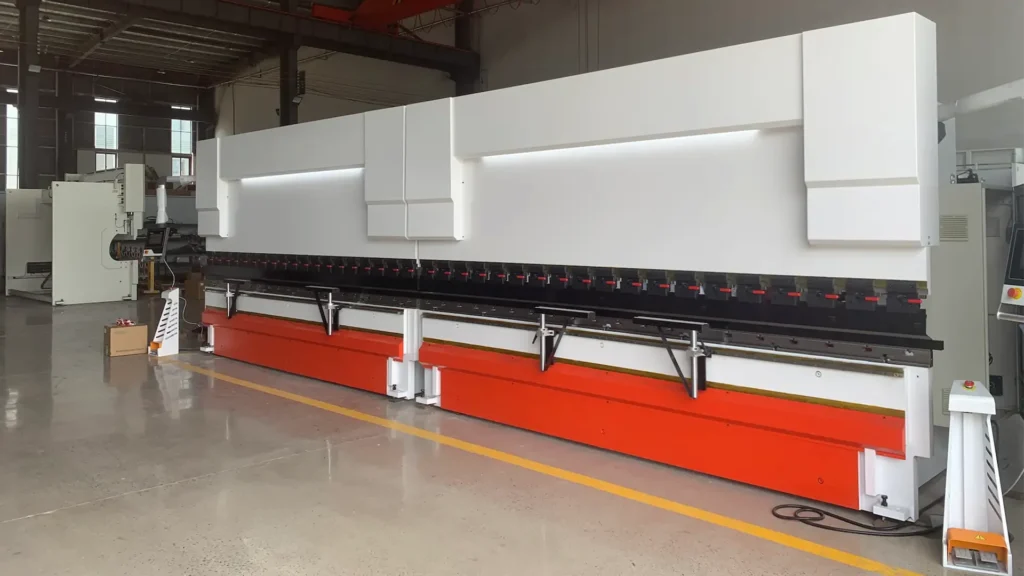

Advantages of Tandem Press Brakes Over Traditional Methods
When compared to manual bending or single-machine setups, tandem press brakes offer a suite of compelling advantages that directly address common pain points in metal fabrication. One of the most notable benefits is their high level of automation, which allows for completing multiple bending sequences in a single operation. This not only speeds up the process but also minimizes human error, ensuring consistent results across batches.
For instance, in terms of accuracy, these machines can control bending angles with tolerances as tight as ±0.5 degrees, far surpassing what manual methods or older equipment might achieve. The precision stems from advanced control systems that monitor every aspect of the bend in real-time, reducing defects and rework. Cost-wise, while the initial investment might seem substantial, tandem setups often prove more economical in the long run. They require less floor space than a massive single press brake and are easier to transport and install, cutting down on setup expenses by up to 30-40% in some cases.
Another key edge is flexibility. Unlike rigid single-length machines, tandem press brakes can operate in synchronized mode for long parts or independently for smaller ones, effectively doubling output when handling shorter workpieces. This adaptability is particularly valuable in job shops where part sizes vary widely. Additionally, they mitigate risks associated with downtime—if one unit needs maintenance, the other can continue producing smaller items, preventing complete halts in workflow.
From a cost-saving perspective, tandem systems lower labor requirements by automating repetitive tasks, allowing operators to focus on oversight rather than manual adjustments. In high-volume environments, this can translate to significant savings, with reports indicating up to 40% improvements in overall efficiency. However, to maximize these benefits, it’s essential to establish robust management protocols. This includes regular calibration checks and training programs to ensure seamless coordination between the machines, avoiding conflicts that could disrupt production flow.
In summary, the advantages boil down to enhanced automation, superior precision, cost efficiencies, and operational flexibility—making tandem press brakes a smart upgrade for businesses aiming to stay competitive.
Working Principle of Tandem Press Brakes
At its core, the working principle of a tandem press brake revolves around the coordinated effort of two or more individual press brakes, linked through a sophisticated control system to function as a unified entity. This setup is particularly adept at processing large metal sheets, where synchronization ensures uniform bends across extended lengths.
The process begins with the input stage, where the metal material—such as steel or aluminum sheets—is fed into the machine via automated loaders or manual positioning. Once secured on the worktable, the system engages the regulator component, which is essentially the heart of the bending operation. Here, hydraulic cylinders or electric servos drive the ram downward, pressing the sheet against the die to form the desired angle. In a tandem configuration, both machines’ rams descend in perfect harmony, monitored by linear encoders and scales that check positions multiple times per second—often up to thousands of readings per millisecond.
The CNC (Computer Numerical Control) system plays a pivotal role, acting as the brain that orchestrates this linkage. It processes input parameters like bend angle, material thickness, and length, then adjusts hydraulic flow or servo motors accordingly to maintain precision. For example, if a slight deviation is detected in one machine, the system compensates instantly to keep the entire bend straight and accurate. Backgauges, which position the sheet accurately, and crowning devices, which compensate for machine deflection, further enhance this process, ensuring consistency even on parts up to 60 feet long.
Once the bend is complete, the output device—typically conveyor systems or robotic arms—removes the finished part for inspection or further processing. This seamless integration not only boosts speed but also reduces material waste, as the machines can handle complex multi-angle bends in one pass.
To illustrate, consider bending a 10-meter structural beam: In tandem mode, the two brakes divide the workload, applying even pressure along the length to avoid warping. Switching to single mode for smaller tasks is straightforward, with the CNC allowing quick reprogramming. Proper maintenance, such as aligning the beds and rams, is crucial to prevent issues like off-center loading, which could stress components over time.
Overall, this principle of synchronized collaboration transforms tandem press brakes into powerhouse tools for demanding fabrication tasks, blending mechanical prowess with digital intelligence.

Application Scenarios for Tandem Press Brakes
Tandem press brakes excel in scenarios where size, precision, and volume intersect, making them indispensable across multiple industries. Their ability to bend ultra-long or thick sheets without splicing opens doors to applications that traditional equipment can’t touch.
In the electronics sector, these machines are frequently used for crafting enclosures and casings for devices like tablet computers. The high accuracy ensures components fit perfectly, reducing assembly issues and enhancing product durability. Similarly, in appliances, tandem setups handle parts for items like washing machines, where large panels require uniform bends to maintain structural integrity.
The automotive industry benefits immensely, with tandem press brakes forming chassis components, body panels, and structural elements. For example, bending long beams for electric vehicle frames demands the precision that tandem systems provide, minimizing weight while maximizing strength. In mechanical manufacturing, they’re ideal for producing machinery parts, such as frames for industrial equipment, where custom angles and tight tolerances are non-negotiable.
Beyond these, broader applications include architectural decoration, where ultra-long metal facades for buildings are bent in one go to ensure seamless aesthetics. In transportation, they form railway car bodies or ship hull sections, improving efficiency by avoiding multiple welds. Energy sectors use them for wind turbine towers and electrical enclosures, leveraging the machines’ capacity for heavy-gauge materials.
A real-world case: Fabricators in the construction machinery field often employ tandem press brakes to create large housings for excavators, achieving 30-40% faster production compared to segmented methods. To optimize usage, companies should develop tailored production plans, factoring in material types and batch sizes to avoid bottlenecks.
In essence, tandem press brakes thrive in high-stakes environments requiring scale and exactness, from consumer goods to heavy infrastructure.
Structural Features of Tandem Press Brakes
The robust design of tandem press brakes underpins their performance, featuring elements that prioritize adaptability, reliability, and ease of use. Central to this is the adjustable bending mechanism, which allows operators to fine-tune angles based on specific job requirements—ranging from sharp 90-degree folds to subtle curves.
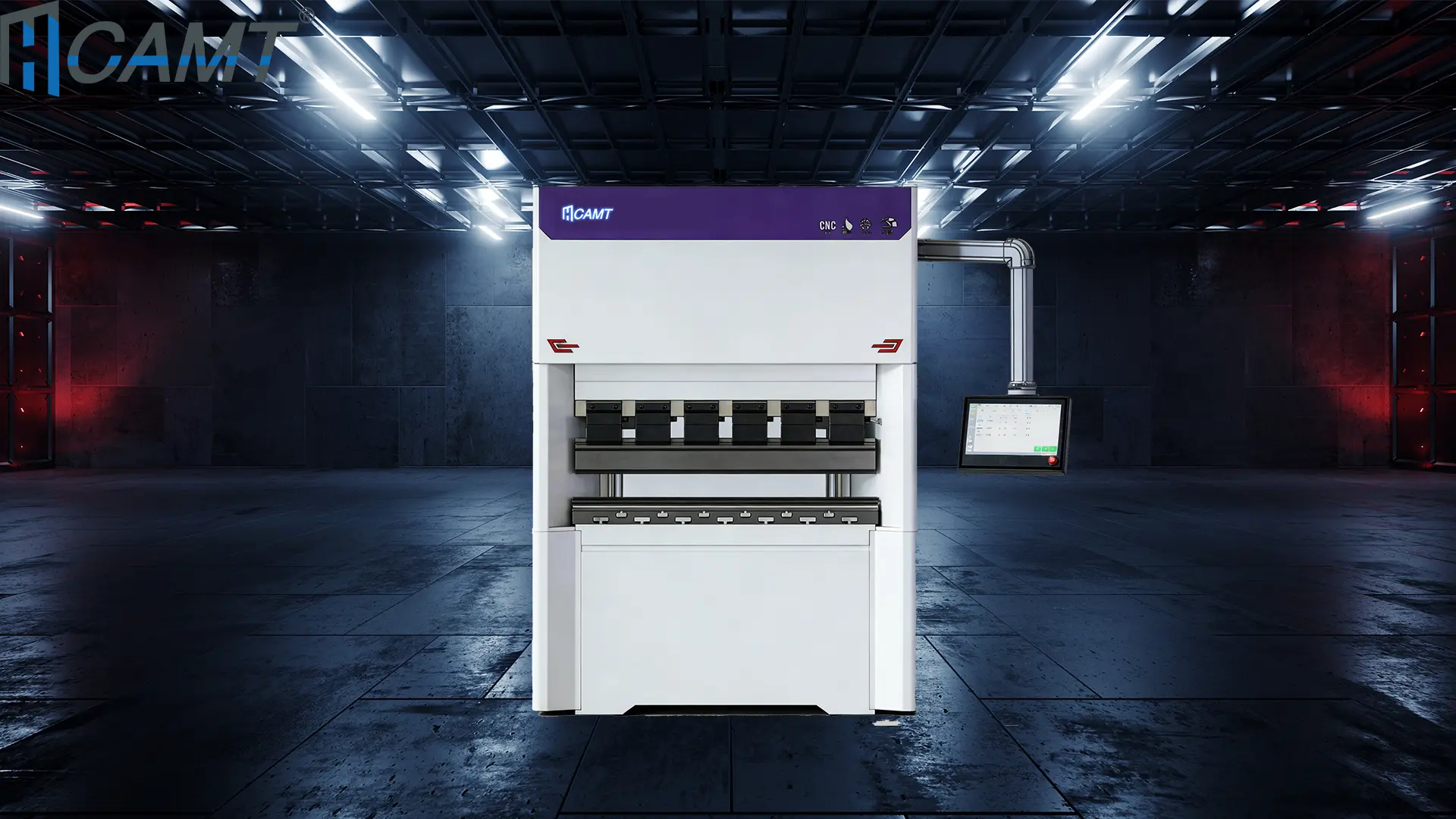
A standout feature is the integrated CNC system, which not only synchronizes the machines but also provides high accuracy through real-time feedback loops. This includes linear encoders for precise positioning and hydraulic valves that respond swiftly to adjustments, ensuring bends stay within minimal error margins.
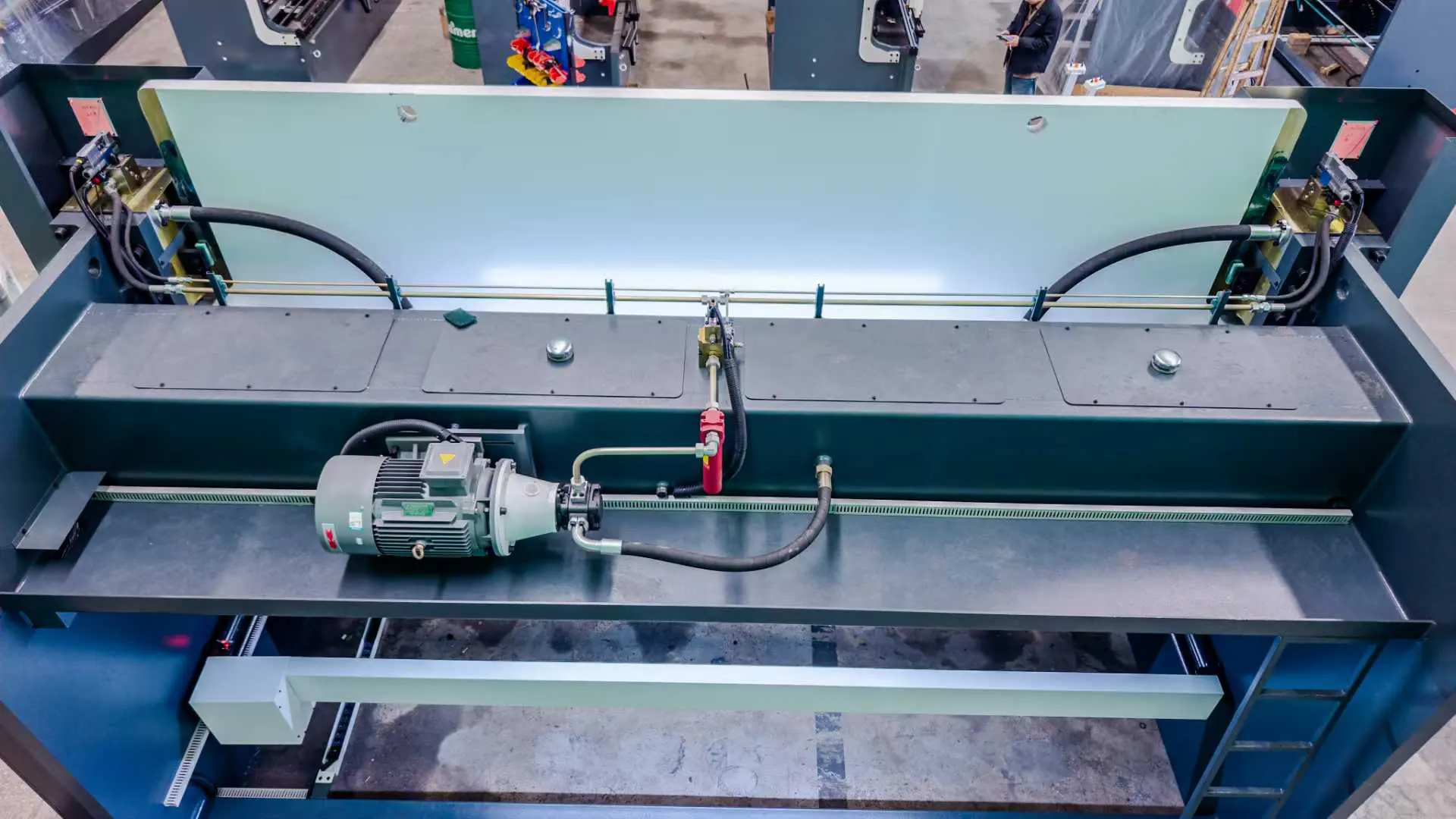
The overall integration is impressive: Components like side housings, rams, and beds are engineered for stability, with the entire setup occupying less space than equivalent single large machines. Maintenance is simplified thanks to modular designs, allowing quick access to parts without extensive disassembly. Reliability comes from durable materials and fail-safes, such as overload protection, that prevent damage during operation.
For enhanced functionality, many models include auxiliary tools like heavy-duty backgauges and automated material handling systems, which streamline workflows for long parts. These features collectively make tandem press brakes a versatile choice, capable of handling diverse materials from thin aluminum to thick steel plates.
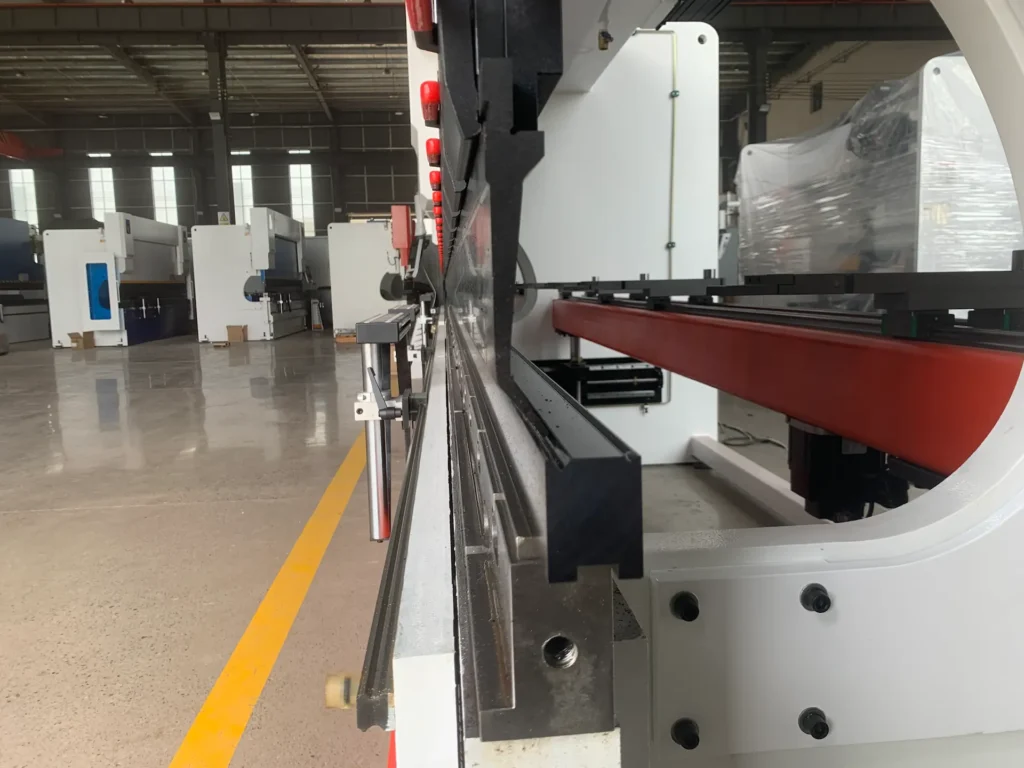

Market Prospects and Future Trends for Tandem Press Brakes
As technology advances, tandem press brakes are poised to become even more integral to metal processing. Currently, they dominate in sectors valuing efficiency, with market growth driven by rising demand for large-scale components in renewable energy and electric vehicles.
Looking ahead, integration with artificial intelligence and industrial robotics will expand their capabilities. AI could enable predictive maintenance, reducing downtime by forecasting issues before they arise, while robotic arms might automate loading and unloading for fully unmanned operations. This evolution aligns with Industry 4.0 trends, where smart factories prioritize connectivity and data-driven decisions.
Market analyses suggest steady expansion, with tandem setups offering better ROI than oversized single machines due to their flexibility and lower risks. As global manufacturing shifts toward sustainability, these machines’ efficiency in minimizing waste will further boost adoption.
In conclusion, tandem press brakes represent a pinnacle of automation in metal bending, delivering unmatched efficiency, precision, and versatility across industries. With ongoing innovations in AI and robotics, their market potential is boundless, promising even greater advancements for forward-thinking manufacturers.
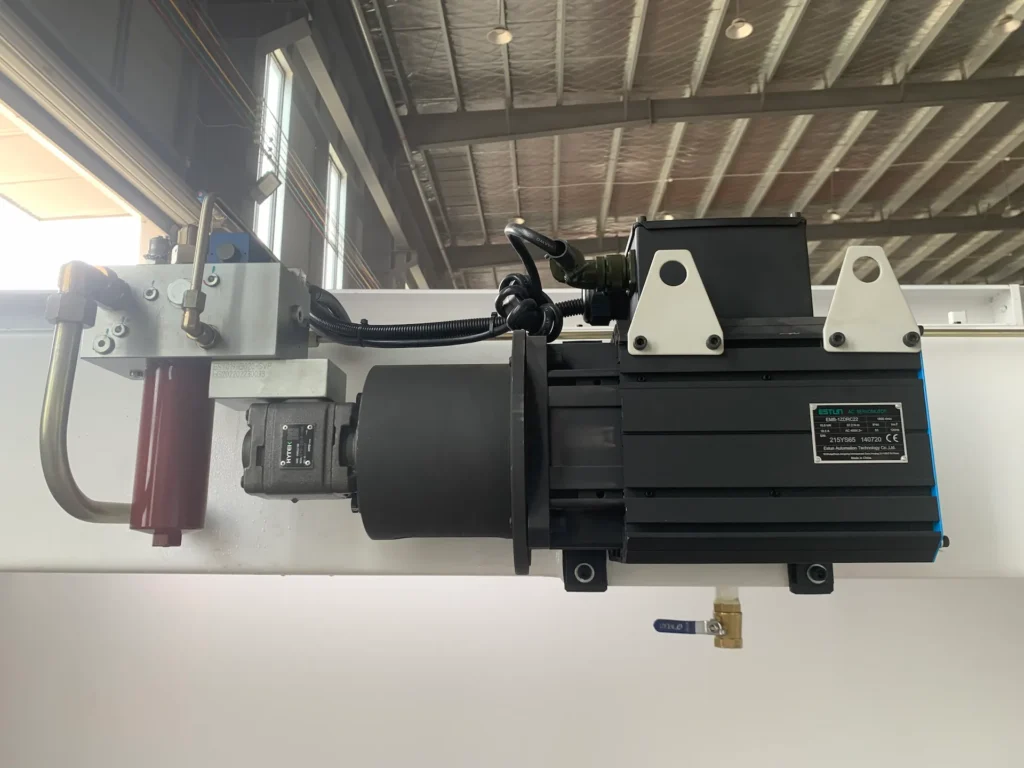

Why Choose CAMT Tandem Press Brakes: Expanded Advantages and Unique Benefits
Building on the general strengths of tandem press brakes, opting for CAMT models elevates these benefits through specialized engineering and innovative features tailored for demanding industrial applications. CAMT, a leader in CNC bending solutions, integrates cutting-edge technology to deliver preferential quality with a notably low error rate, making it an ideal choice for manufacturers prioritizing reliability and performance. Their dual linkage press brakes are designed for bending ultra-long and ultra-wide plates, such as those exceeding 8 meters, commonly used in heavy sectors like shipbuilding, bridge construction, and architectural frameworks.
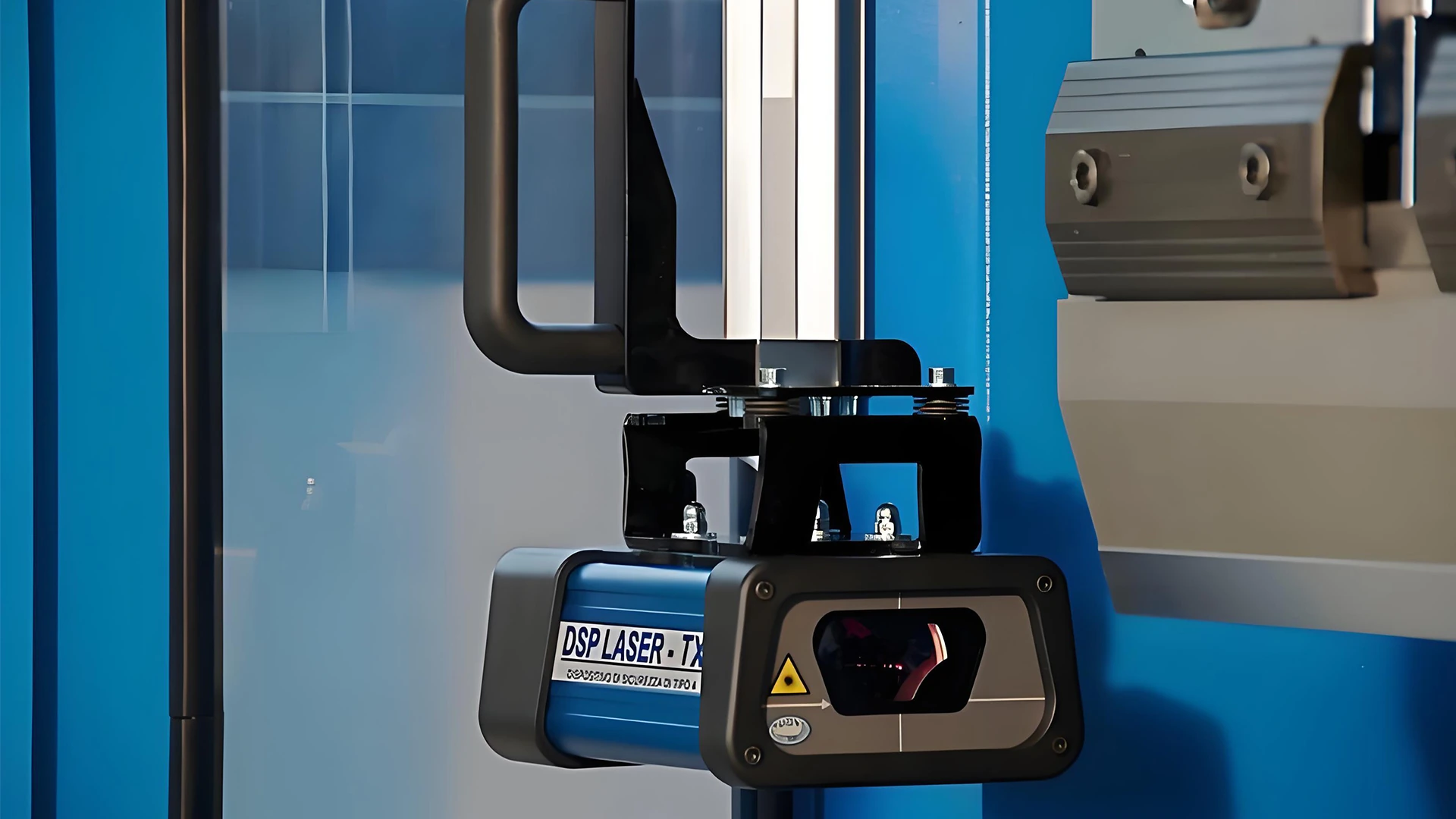
One standout advantage is the superior precision achieved via imported components like the Italy-sourced GIVI MISURE magnetic ruler, which offers 1μm resolution and non-contact operation for exceptional positioning accuracy, even in harsh environments. Paired with the Germany BOSCH-REXROTH hydraulic system and proportional valves, CAMT machines ensure bending accuracy down to ±0.01mm, minimizing deviations and ensuring uniform force distribution to prevent workpiece deformation. This closed-loop control with real-time feedback and error correction outperforms standard setups, resulting in consistent quality across diverse materials and complex multi-stage bends.
Efficiency is another core benefit, with CAMT’s fully ESTUN FULL SERVO/DRIVE system and DELEM DA53T Touch CNC System enabling faster working cycles. The synchronized dual-machine operation allows simultaneous processing of multiple workpieces or large single pieces, significantly reducing production time and boosting throughput. For example, the ability to handle extreme loads up to 600 tons while maintaining Y1/Y2 synchronization enhances stability, allowing for quicker setup and fewer adjustments compared to traditional single-machine alternatives.
Eco-friendliness sets CAMT apart, with proportional valves and servo systems delivering 20%-30% energy savings over conventional hydraulic presses, aligning with sustainable manufacturing goals without compromising power. This not only lowers operational costs but also reduces environmental impact, making it a forward-thinking choice for green initiatives in industries like automotive and electronics.
Flexibility and smart integration further enhance the appeal. CAMT’s IIoT platform and intelligent control hub support multi-protocol compatibility, enabling seamless plug-and-play with existing systems for smart manufacturing automation. The DELEM DA Series Offline Programming Software, including Profile-T3D for 3D simulations, optimizes tool configurations, detects collisions in advance, and streamlines programming—cutting integration costs and accelerating workflows. Finite Element Analysis (FEA) during design verifies performance under stress, mitigating risks of fatigue or fracture for long-term durability.
In terms of maintenance and support, CAMT models boast low-maintenance designs with robust resistance to interference, complying with CE and ISO standards. Overseas after-service ensures minimal downtime, while the machines’ modular structure simplifies repairs. This reliability, combined with over a decade of R&D in CNC controls, provides a unique edge for high-end applications requiring intricate angles and precision.
Overall, choosing CAMT tandem press brakes means investing in a solution that amplifies general tandem advantages with specialized precision, energy efficiency, and intelligent features—ideal for scaling operations in competitive markets.
Metalworking specialist with 12 years of experience in sheet metal fabrication and press brake applications, certified by ASME.