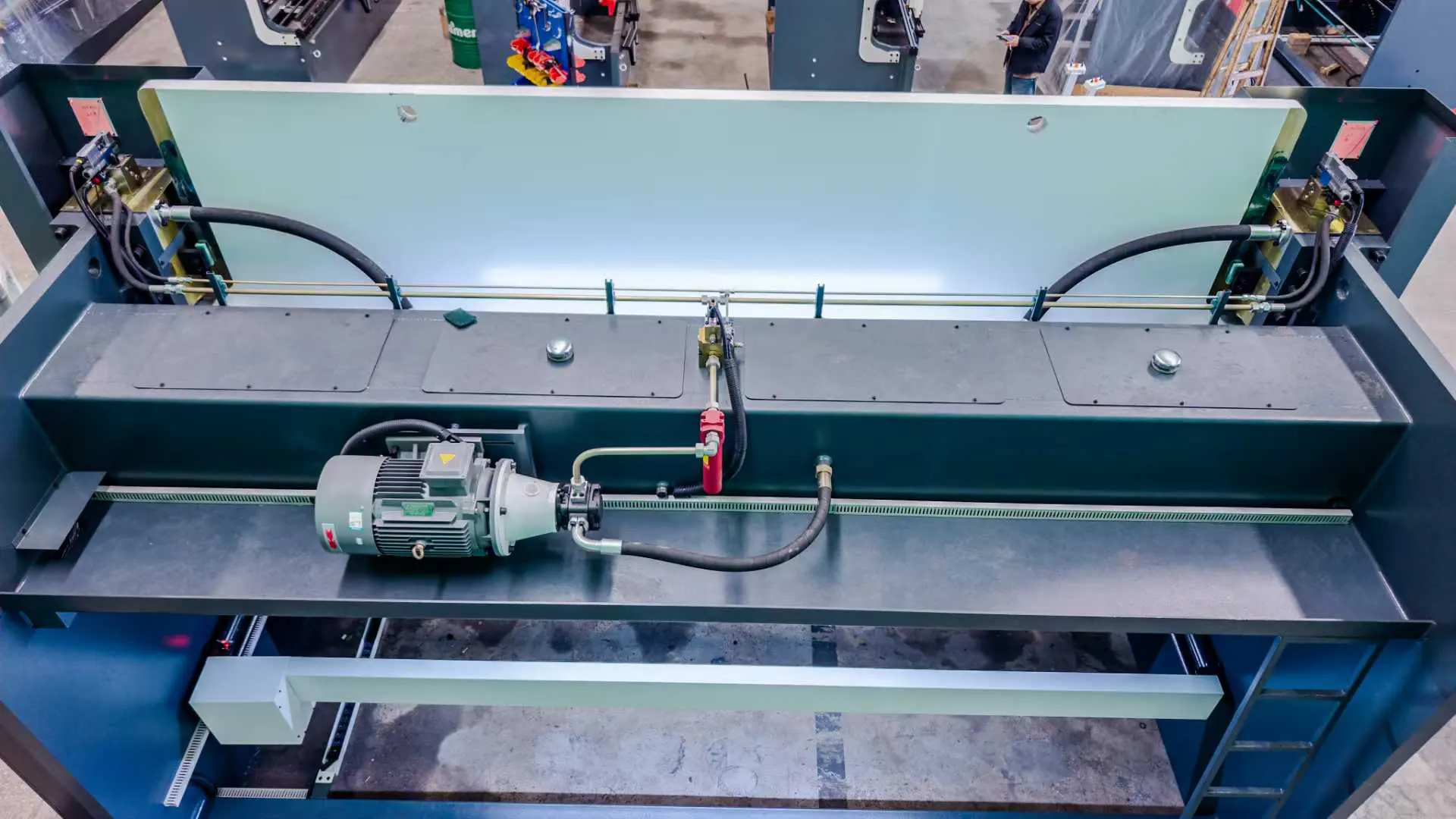
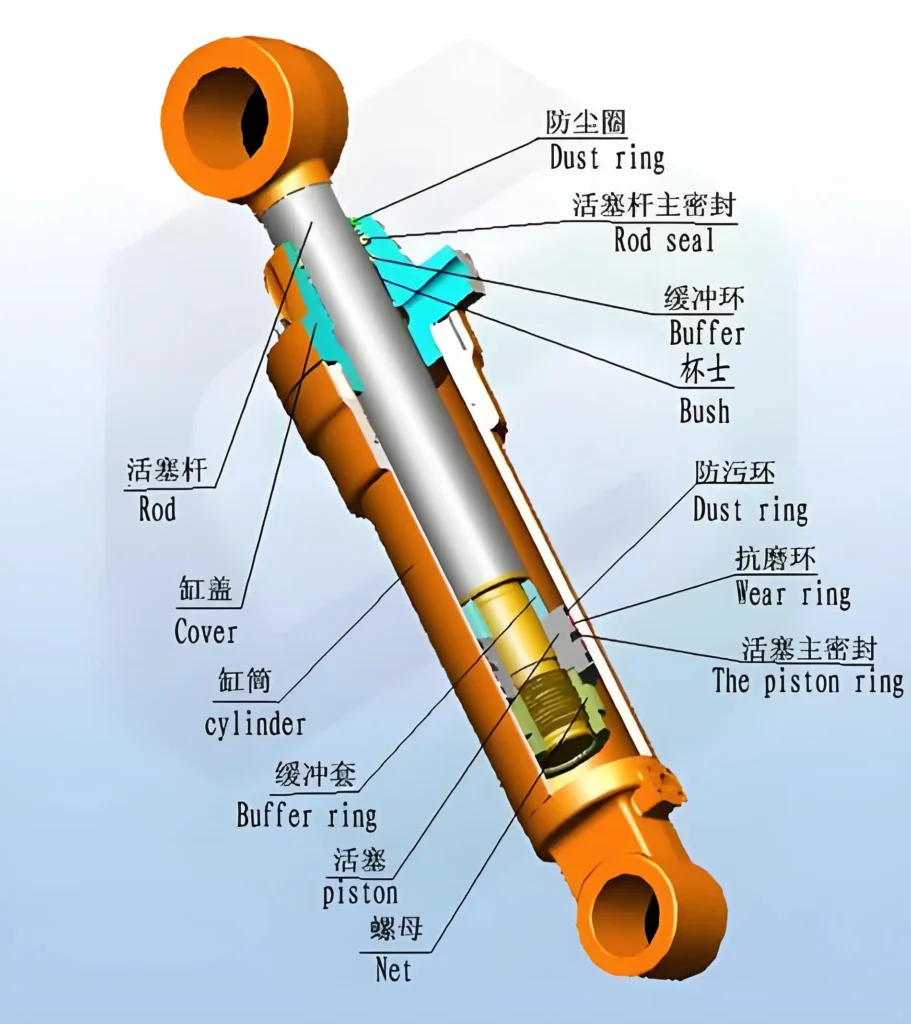
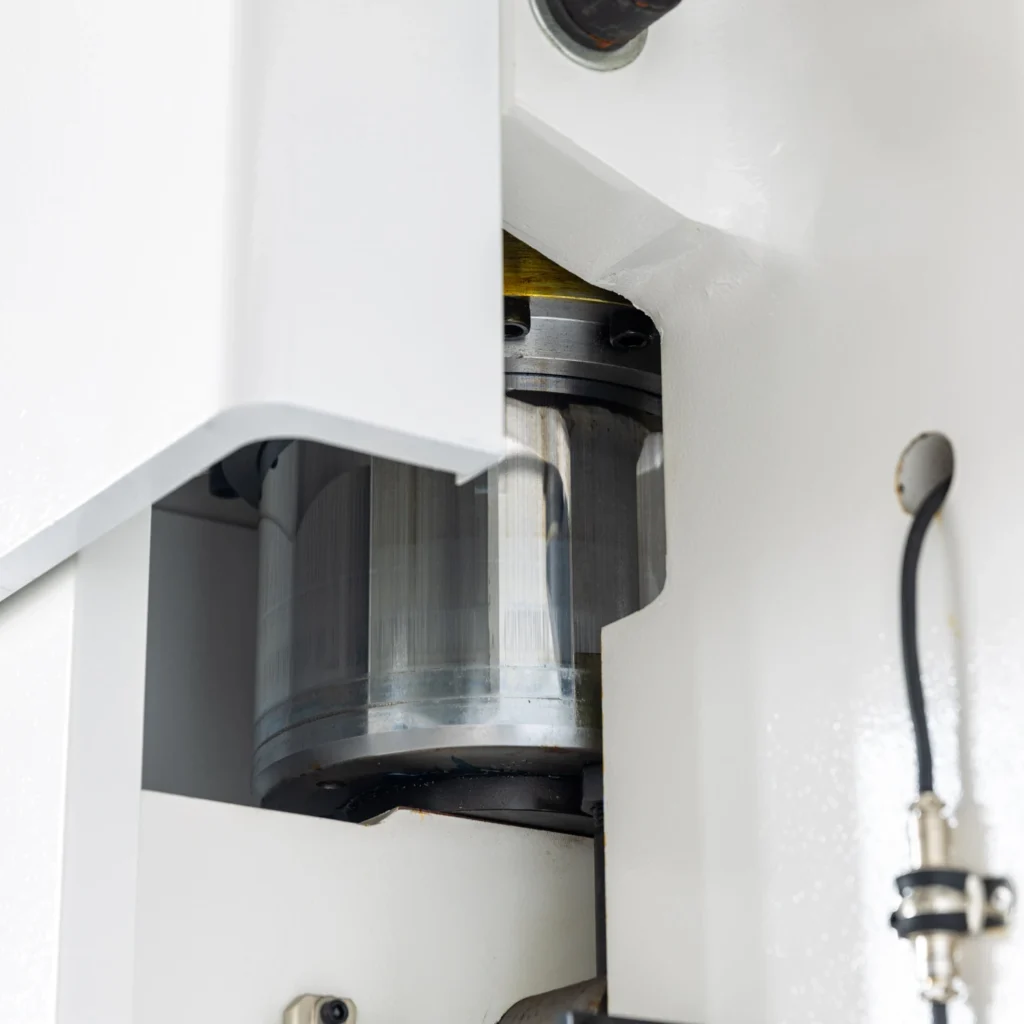
How to Diagnose and Repair Press Brake Cylinder Failures
Impact: Reduces synchronization errors to <0.1mm. Mechanical Component Inspection. Guide Rail and Ram Check.
Clean rails with degreasers and inspect for wear or scratches.
Adjust rail-ram clearance to 0.05-0.1mm for smooth motion.
Cost: $100-$500 for rail repairs.
Load Balance Verification.
Ensure molds are level using a laser alignment tool.
Position workpieces symmetrically to prevent single-sided loading.
Electrical Control Calibration
Sensor Signal Check.
Clean position sensor heads and recalibrate zero points.
Use shielded cables to eliminate signal interference.
Controller Parameter Tuning
Optimize PID settings (e.g., proportional gain: 0.8-1.2, integral time: 0.1-0.2s). | Implement master-slave or cross-feedback algorithms for real-time synchronization. | System Testing and Validation |
Manual Mode Testing | Drive each cylinder individually, monitoring pressure with a gauge (±1 bar tolerance). | Adjust valves to equalize pressures. |
Automatic Mode Calibration | Run self-learning cycles to set synchronization baselines. | Use diagnostic software to monitor displacement curves, targeting <0.1mm error. |
Preventive Maintenance Schedule | Task. | Frequency. |
Cost Estimate | Impact. | Replace hydraulic oil and filters. |
Every 6 months.
Reduces contamination by 80%
Inspect servo valve response.
Quarterly
Prevents 90% of valve-related failures
Lubricate mechanical components
Monthly.
Extends component life by 30%
Log and analyze fault data.
$0 (in-house)
Predicts 70% of potential failures.
FAQ: Press Brake Cylinder Failure Diagnosis and Solutions
Q: What are the main causes.
of press brake cylinder failure?
A: Valve core sticking, blockages, low control pressure, air in the system, or high fluid viscosity in cold conditions.
Q: How do I fix a stuck valve core or blocked valve hole?
A: Check fluid for contamination, clean or replace the valve core, and inspect valve body wear. Q: Why does the cylinder not move or move slowly?.
A: Inspect for tight seals, contamination, or misalignment. Replace worn seals and ensure proper cylinder alignment. Q: How can I address low hydraulic pressure?.
A: Adjust throttling resistance, verify valve settings, and check pressure source for interference. Q: How do I prevent air in the hydraulic system?.
A: Monitor fluid levels, inspect pump suction seals, and clean/replace coarse filters. Q: Why is cylinder performance poor in cold conditions?.
A: High fluid viscosity reduces flow. Use low-viscosity hydraulic oil or preheat the system with a heater.
A: Check fluid for contamination, clean or replace the valve core, and inspect valve body wear. A: Follow a quarterly maintenance schedule, including fluid checks, seal inspections, and valve calibrations.
A: Inspect for tight seals, contamination, or misalignment. Replace worn seals and ensure proper cylinder alignment. press brake cylinder.
press brake safety Every 6 months.
Reduces contamination by 80%
A: Check fluid for contamination, clean or replace the valve core, and inspect valve body wear. Quarterly.
Prevents 90% of valve-related failures Lubricate mechanical components.
Monthly Extends component life by 30%.
Log and analyze fault data
A: Check fluid for contamination, clean or replace the valve core, and inspect valve body wear. Predicts 70% of potential failures.
A: Inspect for tight seals, contamination, or misalignment. Replace worn seals and ensure proper cylinder alignment. Q: What are the main causes.
of press brake cylinder failure? A: Valve core sticking, blockages, low control pressure, air in the system, or high fluid viscosity in cold conditions.
Q: How do I fix a stuck valve core or blocked valve hole?.
A: Check fluid for contamination, clean or replace the valve core, and inspect valve body wear.
Q: Why does the cylinder not move or move slowly?
A: Inspect for tight seals, contamination, or misalignment. Replace worn seals and ensure proper cylinder alignment.
Q: How can I address low hydraulic pressure?
A: Adjust throttling resistance, verify valve settings, and check pressure source for interference.
Q: How do I prevent air in the hydraulic system?.
A: Monitor fluid levels, inspect pump suction seals, and clean/replace coarse filters.
Q: Why is cylinder performance poor in cold conditions?
A: High fluid viscosity reduces flow. Use low-viscosity hydraulic oil or preheat the system with a heater.
Q: How often should I maintain my press brake cylinder?.
A: Follow a quarterly maintenance schedule, including fluid checks, seal inspections, and valve calibrations.
Press brake cylinder maintenance is a cornerstone of reliable sheet metal fabrication. By addressing failure causes like contamination, air bubbles, and seal issues, and implementing systematic synchronization solutions, operators can achieve near-perfect bending accuracy and efficiency. Regular maintenance, supported by data-driven schedules and professional services like CAMT, can extend equipment lifespan by 3-7 years and reduce downtime costs by up to 40%. Invest in high-quality components and proactive care to keep your hydraulic or CNC press brake performing at its best.
Read more about Principle and Function of Press Brake Safety Protection System.
Read more about Press Brake Maintenance and Repair.
Read more about Practical Methods for Press Brake Accuracy with Long Term Precision.
Read more about Practical Guidance For Press Brake Operation
Read more about How to Properly Install a Press Brake Machine.
press brake cylinder.
Impact: Reduces synchronization errors to <0.1mm.
Mechanical Component Inspection
Guide Rail and Ram Check
Clean rails with degreasers and inspect for wear or scratches.
Adjust rail-ram clearance to 0.05-0.1mm for smooth motion.
Cost: $100-$500 for rail repairs.
Load Balance Verification
Ensure molds are level using a laser alignment tool.
Position workpieces symmetrically to prevent single-sided loading.
Electrical Control Calibration
Sensor Signal Check
Clean position sensor heads and recalibrate zero points.
Use shielded cables to eliminate signal interference.
Controller Parameter Tuning
Optimize PID settings (e.g., proportional gain: 0.8-1.2, integral time: 0.1-0.2s).
Implement master-slave or cross-feedback algorithms for real-time synchronization.
System Testing and Validation
Manual Mode Testing
Drive each cylinder individually, monitoring pressure with a gauge (±1 bar tolerance).
Adjust valves to equalize pressures.
Automatic Mode Calibration
Run self-learning cycles to set synchronization baselines.
Use diagnostic software to monitor displacement curves, targeting <0.1mm error.

Preventive Maintenance Schedule
Task | Frequency | Cost Estimate | Impact |
Replace hydraulic oil and filters | Every 6 months | $200-$500 | Reduces contamination by 80% |
Inspect servo valve response | Quarterly | $100-$300 | Prevents 90% of valve-related failures |
Lubricate mechanical components | Monthly | $50-$150 | Extends component life by 30% |
Log and analyze fault data | Monthly | $0 (in-house) | Predicts 70% of potential failures |
FAQ: Press Brake Cylinder Failure Diagnosis and Solutions
Q: What are the main causes of press brake cylinder failure?
A: Valve core sticking, blockages, low control pressure, air in the system, or high fluid viscosity in cold conditions.
Q: How do I fix a stuck valve core or blocked valve hole?
A: Check fluid for contamination, clean or replace the valve core, and inspect valve body wear.
Q: Why does the cylinder not move or move slowly?
A: Inspect for tight seals, contamination, or misalignment. Replace worn seals and ensure proper cylinder alignment.
Q: How can I address low hydraulic pressure?
A: Adjust throttling resistance, verify valve settings, and check pressure source for interference.
Q: How do I prevent air in the hydraulic system?
A: Monitor fluid levels, inspect pump suction seals, and clean/replace coarse filters.
Q: Why is cylinder performance poor in cold conditions?
A: High fluid viscosity reduces flow. Use low-viscosity hydraulic oil or preheat the system with a heater.
Q: How often should I maintain my press brake cylinder?
A: Follow a quarterly maintenance schedule, including fluid checks, seal inspections, and valve calibrations.
Press brake maintenance and repair should be viewed as an ongoing process rather than a reaction to failure. Proper lubrication, careful hydraulic system management, and regular mechanical inspection form the foundation of reliable machine operation. These practices not only reduce downtime but also help maintain consistent bending accuracy over the machine’s service life.
Press brake cylinder maintenance is a cornerstone of reliable sheet metal fabrication. By addressing failure causes like contamination, air bubbles, and seal issues, and implementing systematic synchronization solutions, operators can achieve near-perfect bending accuracy and efficiency. Regular maintenance, supported by data-driven schedules and professional services like CAMT, can extend equipment lifespan by 3-7 years and reduce downtime costs by up to 40%. Invest in high-quality components and proactive care to keep your hydraulic or CNC press brake performing at its best.
V-Grooving Machine
- Press Brake
- Laser Cutting Machine
- Shearing Machine
- Press Brake Safety Precautions: Complete Guide for Safe Operation and Maintenance
- Hydraulic Press Machine
- Read more about Practical Methods for Press Brake Accuracy with Long Term Precision
- Rolling Machine
- Ironworker
- Press Brake Tooling
- Machinery Accessories